What is Economics, Macroeconomics and Microeconomics
Economics
Economics is the study of the social science that studies the production, Distribution and consumption of goods and services. Economics helps those who know it to understand global issues such as wars between Nations, Civil wars, Inflation, Reflation, Deflations and its effects on lives of people. We study Economics because resources are scarce and needs are unlimited.
There are two sides to the study of Economics:
- Microeconomics(Demand and Supply)
- Macroeconomics(Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply)
Microeconomics
Microeconomics is derived from the Greek prefix "Mikro" means "Small". In Microeconomics we study the income of an Individual.
Microeconomics focuses on supply and demand and other forces that determine the price levels in the economy. It takes what is referred to as a bottom-up approach to analyzing the economy. In other words, microeconomics tries to understand human choices and resource allocation.
Studies
- Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium- Prices are determined by the theory of supply and demand. Under this theory, suppliers offer the same price demanded by consumers in a perfectly competitive market. This creates economic equilibrium.
- Production Theory- This is the study of production. The economic process of converting inputs into outputs.
- Costs of Production- According to this theory, the price of goods or services is determined by the cost of the resources used during production.
- Labor Economics- This principle looks at workers and employers, and tries to understand the pattern of wages, employment, and income.
- Opportunity Cost- Next best alternative thing one may have.
key Points
- Microeconomics focuses on supply and demand, and other forces that determine price levels, making it a bottom-up approach.
- Macroeconomics takes a top-down approach and looks at the economy as a whole, trying to determine what the economy should look like.
- Investors can use microeconomics in their investment decisions, while macroeconomics is an analytical tool mainly used to craft economic and fiscal policy.
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics is derived from the Greek Prefix "Makro" means "Large". In Macroeconomics we study the national economy of a country as a whole.
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that studies how an overall economy works. Macroeconomics studies economy-wide phenomena such as Inflation, Change in Price, Economic Growth, National Income, Gross Domestic Product(GDP), Regional economy, Global Economy etc.
As the term implies, macroeconomics looks at the overall, big-picture scenario of the economy or in simple words we can say looks as a whole and then analyzes how different sectors of the economy relate to one another to understand how the aggregate functions. This includes looking at variables like unemployment, GDP, and inflation.
In short Macroeconomics, we study National income, total income in the economy, deals with aggregate decisions and analyze economy as whole.
Limitations of Macroeconomics
It is also important to understand the limitations of economic theory. Theories are often created in a vacuum and lack certain real-world details like taxation, regulation and transaction costs. The real world is also decidedly complicated and their matters of social preference and conscience that do not lend themselves to mathematical analysis.
Even with the limits of economic theory, it is important and worthwhile to follow the major macroeconomic indicators like GDP, inflation and unemployment. The performance of companies, and by extension their stocks, is significantly influenced by the economic conditions in which the companies operate and the study of macroeconomic statistics can help an investor make better decisions and spot turning points.
Economic Growth
Economic growth refers to an increase in aggregate production in an economy. Macroeconomists try to understand the factors that either promote or retard economic growth in order to support economic policies that will support development, progress, and rising living standards.
key Points
- Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that deals with the structure, performance, behavior, and decision making of the whole, or aggregate, economy.
- The two main areas of macroeconomic research are long-term economic growth and shorter-term business cycles.
- Macroeconomics in its modern form is often defined as starting with John Maynard Keynes and his theories about market behavior and governmental policies in the 1930s; several schools of thought have developed since.
Difference between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics studies individual units and business decisions, while macroeconomics analyzes the decisions made by countries and governments.
- In Macroeconomics focus is on whole economy or studies economy as a whole whereas, microeconomics is more focused on the individual factors of the economy (people, company, industry etc).
- Microeconomics known as Price Theory whereas, Macroeconomics is known as Income theory.
- Microeconomics is concerned with the optimization goals of the individual consumers and producers whereas, Macroeconomics is concerned with the optimization of the growth process of the entire economy.
- Microeconomics particularly focus on Price analysis whereas, Macroeconomics focus on Income analysis.
- Microeconomics analysis is simple whereas, Macroeconomics is complex due to the study of large groups.
- Microeconomics include demand and supply of individuals whereas, Macroeconomics include aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
- Microeconomics studies Individual income whereas, Macroeconomics studies National Income.

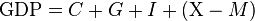


Comments
Post a Comment