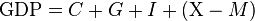What is Stagflation

Stagflation Meaning A period of slow economic growth and high unemployment (stagnation) while prices rise (inflation) or Stagflation is an economic situation where the growth rate slows down, unemployment levels remain steadily high & inflation also stays high. In economics, the English word Stagflation refers to a situation when both the inflation rate and the unemployment rate remain high. This is a financially difficult situation for a country, since, at the moment both inflation and economic stability problems arise simultaneously and no macroeconomic policy can simultaneously focus on these problems at the same time can. The origin of the word stagflation consisting of two-word sounds is generally attributed to British politician Len McLeod, who coined the term in 1965 during one of his speeches in the parliament there. This concept is also notable partly because, in the post-war macro-economic theory, Inflation and recession were considered to be mutually exclusiv